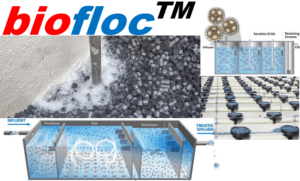
Package Sewage treatment plant
Package Sewage treatment plant and importance of phosphorus removal is a well known fact. As per Philippines DENR RA 9275 Clean Water Act under its latest Regulation DAO 2016-08 on general effluent Standard total phosphorus (TP) effluent limit is 1 mg/L. Utilities that need to meet these lower limits will want to consider enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR). Phosphorus removal during wastewater treatment is vital to ensuring public safety and protecting the environment. Removal of this nutrient from waste streams is key to preventing eutrophication – a natural process inciting algae blooms. Algae blooms can suffocate ecosystems, creating dead zones in which animal life cannot survive. Moreover, this causes other water quality issues threatening our drinking water.
Avlon wastewater treatment plants use two strategies to remove phosphorus: chemical phosphorus removal (CPR) and biological phosphorus removal (BPR).
Chemical phosphorus removal (CPR):
Chemical phosphorus removal from package Sewage treatment plant typically involves precipitating influent phosphorus with an iron or aluminum salt. Using an iron salt, such as ferric chloride, provides the ancillary benefits of reducing scum in secondary treatment and managing sulfides and odors in anaerobically digested sludge. Chemical addition can also limit struvite formation, which can become an issue when a plant converts to a BPR system and more phosphorus is released in the digester. Disadvantages of CPR include storage requirements and sludge production increases 20% to 30% of chemical Dose and other physical parameters
The required chemical dose is related to the liquid phosphorus concentration. For target concentrations above 2 mg/L (appropriate for chemical addition to a primary clarifier), a dose of 1.0 mole of aluminum or iron per mole of phosphorus is sufficient. For lower phosphorus concentrations in the range of 0.3 – 1.0 mg/L, the dose can be in the range of 1.2 to 4.0 moles aluminum or iron per mole of phosphorus. The pH value is an important factor for efficient removal of phosphorus using alum or other salts, as the solubility of their precipitates vary with pH. Phosphorus removal is most efficient in the pH range of 5 to 7 for alum and of 6.5 to 7.5 for ferric salts since their precipitates will not readily return to solution.
Enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR):
EBPR is simply the biological uptake of phosphorus by selected microorganisms called phosphorus-accumulating organisms (PAOs). While the actual uptake of phosphorus occurs under aerobic conditions, PAOs must first be conditioned by exposure to volatile fatty acids (VFA) under anaerobic conditions. PAOs store food under anaerobic conditions and then process the stored food once under aerobic conditions. So to simply it, The EBPR process in the package Sewage treatment plant works by providing an anaerobic zone with an ample supply of readily biodegradable carbonaceous oxygen demand. Organic matter in the anaerobic zone is fermented to create a source of volatile fatty acids (VFAs), particularly acetate and propionate, which in turn serve as food sources for PAOs
PAOs expend energy to transform VFAs into a chemical form for storage, and they obtain energy for VFA storage by breaking phosphorus bonds within themselves. This results in the release of ortho-phosphate which is the conditioning step needed to trigger the aerobic “luxury phosphorus uptake.” If PAOs are exposed to enough VFA, they will deplete their energy reserves and become stressed. This stress causes PAOs to overreact and accumulate more phosphorus in their chemical energy storage banks.
Influent BOD : P Ration and its importance:
As a rule of thumb, a minimum influent BOD:P ratio of 25:1 is necessary in order to provide adequate conditions for PAOs to thrive. Note that this ratio is applicable to the influent of the anaerobic phase of the EBPR process. Upstream treatment processes such as primary clarification may remove too much BOD for successful PAO conditioning. A more comfortable margin is provided with influent BOD:P ratios of 30:1 to 40:1. Dilute influent characteristics with low BOD concentrations, excessive BOD removal in primary treatment processes and excessive influent or solids dewatering side-stream phosphorus concentrations can cause influent BOD:P ratios to fall below the optimal range for successful EBPR.
Return Activated Sludge (RAS)
RAS in nitrifying systems designed to remove ammonia will contain significant nitrate concentrations that are not compatible with two stage (aerobic/anaerobic) EBPR systems. In these cases, provisions must by made to denitrify the return solids to avoid compromising the integrity of the anaerobic zone. Various de-nitrification EBPR configurations are effective for package Sewage treatment plant with these conditions, most often including one or more anoxic phases where bacterial respiration is dependent on oxygen derived from nitrites or nitrates rather than dissolved oxygen. Waste activated sludge (WAS) is removed from the system in the secondary clarification processes and transferred to solids handling units. PAO and phosphorus rich return activated sludge (RAS) is recycled to the anaerobic zone to build up the population of PAOs in the system and to be reconditioned for another EBPR cycle.
Care to be taken during designing the system
Dissolved Oxygen: Avoid over aeration. Maintain 0.5 to 1.0 mg/L DO concentrations at the end of the aeration zone. This will allow for the activated sludge process to perform adequately and ensure that excessive dissolved oxygen concentrations are not recycled back to the anaerobic phase.
Filamentous Control: Avoid over chlorination. Excessive RAS chlorination can harm the EBPR process. Anaerobic and anoxic selector zones should help control filamentous bacteria by placing them at a competitive disadvantage with respect to other types of bacteria
Influent BOD:P Ratios: A minimum 25:1 ratio of influent BOD to phosphorus has been reported to be critical for successful EBPR. Source reduction of phosphorus loads can help decrease influent phosphorus loads and improve EBPR efficiency.
Recycled P Loads: Evaluate phosphorus concentrations and loads returned to the treatment process from solids dewatering operations. Sludge dewatering return flows can contain significant amount of phosphorus that can effectively increase the influent load to the WWTP and reduce the influent BOD:P ratio sufficiently to overwhelm the EBPR
Secondary Phosphorus Release: This phenomenon occurs in the anaerobic tank if PAOs release stored phosphates but fail to take up available VFAs. This is a problem because subsequent uptake of phosphorus in the aerobic phase will not occur. Causes associated with these conditions include excessive detention times in anaerobic, anoxic or aerobic phases, PAOs settling in primary clarifiers, septic conditions in secondary clarifiers, anaerobic digestion of primary and EBPR sludges, blending of primary and EBPR sludges and failure to aerate stored EBPR sludges.
Combined Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal with Chemical Addition
When chemical addition is used in combination with EBPR, it is generally used as a polishing step, usually in secondary treatment. This approach is preferred when EBPR can provide substantial phosphorus removal, but not enough to meet a required effluent phosphorus concentration limit of 1 mg/L based on a monthly average.
Phosphorus removal is an important process in meeting the DENR RA 9275 Clean Water Act under its latest Regulation DAO 2016-08 on general effluent Standard. Avlon Inc, is a leader in EBPR technologies with a comprehensive product portfolio and experienced professionals to help you find the best options for new sewage treatment or upgrading your existing sewage treatment plant.
Contact us today to talk about nutrient removal solutions! Avlon is one of the Best Manufacturers and Suppliers in Philippines dealing in Wastewater Treatment Plants, package Sewage Treatment Plant. They give Best Quality and Best Customer Service. Check out www.avlon-php.com