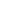Electric Boiler: An In-Depth Guide
What Is an Electric Boiler?
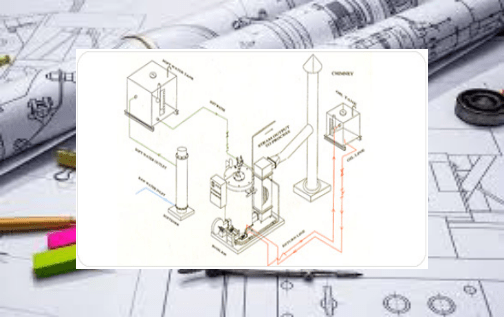
As opposed to the typical boilers, an electric boiler operates without using combustible fuel such as oil, gas, coal or biomass but rather use electricity to generate heat for your home or steam for your production process. When referring to an electric boiler, it implies that electricity is the type of fuel used to power the boiler.
An electric boiler can come in the form of an electric combi boiler, as they both operate on electricity. However, other types such as biomass boilers or gas boilers have a different fuel type.
The electric boiler system is highly efficient thanks to the conversion of electricity into thermal energy that produces an almost 100% efficiency rate. However, it depends how the electricity is generated — whether the electricity generation is efficient or not will influence your conversion efficiency rate.
You will often hear about electric water boilers: be careful, it is not the same as electric boilers! In fact, the first one concerns the small appliance you use to boil water when you want to make a tea or a coffee while the second one involves the device used to heat your home.
If you’re considering the installation of a boiler, we provide you with a free of charge and with no obligation service that allows you to request quotes and compare different systems, so that you can find the most suitable for you. Just fill in the form on the right to request offers.
How Do Electric Boiler Work?
The production of steam is a rather simple process. First, the electricity runs through a heating device that has a resistor property, therefore allowing heat to be created by the resistance phenomenon. Then, when the heat is created, the water comes via a pipe from the water tank to the heating device or close to it to get heated up. When the water is hot enough and starts boiling it produces steam that is used to heat your home via steam pipes.
We could then say that an electric steam boiler works in a similar way as an oil-fired boiler, the difference being the means by which the water is heated.
Pros of Electric Boiler
Several reasons make electric boilers good investments. We listed the main advantages of electric steam boilers:
No need for combustible fuel. Indeed, the use of electric boilers makes the use of a combustion fuel such as gas or oil obsolete. You can, therefore, decrease your energy bill by focusing on electricity rather than diversifying the energy used.
Save space. Because electric boilers don’t use combustion fuel, you do not need to add a fuel storage close to your boiler. Thus, this space left vacant can be used for other purposes.
Save money and energy. Thanks to an electric steam boiler, you benefit from a high-efficiency rate, as almost no energy is lost during the conversion of electricity into thermal energy. You, therefore save money on your energy bill compared to your bill if you possess a condensing boiler such as a fuel combustion one. You also have to install less equipment with an electric steam boiler, which can help you save money during the installation process.
Safe because you do not use fuel for electric boilers, your boiler is safer to use as you won’t experience fuel leaks.
Help conserve the environment. An electricity boiler benefits from a smaller carbon footprint than fuel boiler when it is running.
Reduce your maintenance costs. A combustion boiler needs to get its pipes replaced after some time, mostly when it concerns biomass boilers, wood pellets boilers or wood-fired boiler stoves. However, electric boilers don’t need as much maintenance which saves you time as well as costs.
Cons of Electric Boiler
When referring to the cost of new boiler, there are many factors to take into consideration:
In the previous section, we said that investing in an electric steam boiler is good for the environment. Be careful, this has to be nuanced! Indeed, the generation of heat from an electric boiler compared to a fuel combustion boiler generates less pollution. However, when it comes to producing electricity, it can be as costly for the environment as other fuel extraction such as gas or oil. So the impact of electric boilers on the environment is not always as clear.
This type of boiler operation depends on the generation of power (electricity). If there is a power shortage you might end up with no electricity during some time, making your boiler in-operational.
Your energy bill is mainly subject to the cost of electricity. Nowadays, this cost tends to rise making it more expensive to operate your electric steam boiler. Moreover, with the abandon in some countries of the nuclear power to generate electricity, it might be harder to obtain electricity and thus more expensive.