Boiler contractor Philippines- Avlon Inc, An Introduction
We as responsible Boiler contractor Philippines when it comes to boiler efficiency, we believe in sticking to the facts. The value of buying a higher efficiency boiler will pay dividends every day, every year, throughout the life of the equipment.
Boiler efficiency, in the simplest terms, represents the difference between the energy input and energy output. A typical boiler will consume many times the initial capital expense in fuel usage annually. Consequently, a difference of just a few percentage points in boiler efficiency between units can translate into substantial savings. The efficiency data used for comparison between boilers must be based on proven performance to produce an accurate comparison of fuel usage. So, are you comparing fuel usage with what your boiler suppliers claim of its boiler efficiency? If not then let’s learn today how to do that.
Performance Evaluation of Boiler by Boiler contractor Philippines
The performance of a boiler, which include thermal efficiency and evaporation ratio (or steam to fuel ratio), deteriorates over time for reasons that include poor combustion, fouling of heat transfer area, and inadequacies in operation and maintenance. Even for a new boiler, deteriorating fuel quality and water quality can result in poor boiler performance. Boiler efficiency tests help us to calculate deviations of boiler efficiency from the design value and identify areas for improvement.
The purpose of the performance test is to determine actual performance and efficiency of the boiler and compare it with design values or norms. It is an indicator for tracking day-to-day and season-to-season variations in boiler efficiency and energy efficiency improvements.
For the testing to be done, the boiler should be operated under steady load conditions (generally full load) for a period of one hour after which readings would be taken during the next hour of steady operation to enable the efficiency to be calculated. The efficiency of a boiler is quoted as the % of useful heat available, expressed as a percentage of the total energy potentially available by burning the fuel. This is expressed on the basis of gross calorific value (GCV).
Thermal efficiency
Thermal efficiency of a boiler is defined as the percentage of heat input that is effectively utilized to generate steam. As per ASME Standard: PTC-4-1 Power Test Code for Steam Generating Units, there are two methods of assessing boiler efficiency: direct and indirect.
In the direct method, the ratio of heat output (heat gain by water to become steam) to heat input (energy content of fuel) is calculated.
This is also known as ’input-output method’ due to the fact that it needs only the useful output (steam) and the heat input (i.e. fuel) for evaluating the efficiency. This efficiency can be evaluated using the formula:

Or
![]()
Both heat input and heat output must be measured. The measurement of heat input requires knowledge of the calorific value of the fuel and its flow rate in terms of mass or volume, according to the nature of the fuel.
There are several methods, which can be used for measuring heat output. With steam boilers, an installed steam meter can be used to measure flow rate, but this must be corrected for temperature and pressure as per Boiler contractor Philippines.
The alternative with small boilers is to measure feed water, and this can be done by previously calibrating the feed tank and noting down the levels of water during the beginning and end of the trial. Care should be taken not to pump water during this period. Heat addition for conversion of feed water at inlet temperature to steam, is considered for heat output.
In case of boilers with intermittent blowdown, blowdown should be avoided during the trial period. In case of boilers with continuous blowdown, the heat loss due to blowdown should be calculated and added to the heat in steam.
Evaporation ratio
Evaporation ratio, or steam to fuel ratio, is another simple, conventional parameter to track performance of boilers on-day-to-day basis.
Test Data and Calculation
Water consumption and coal consumption were measured in a coal-fired boiler at hourly intervals. Weighed quantities of coal were fed to the boiler during the trial period. Simultaneously water level difference was noted to calculate steam generation during the trial period. Blow down was avoided during the test. The measured data is given below.
TYPE OF BOILER: COAL FIRED BOILER
Steam Generated : 8 TPH
Steam Pressure : 10 kg/cm2 (g)
Steam Temperature : 1800C
Enthalpy of steam at 10 kg/cm2 (g) : 665 kCal/kg
Feed Water Temperature : 850C
Enthalpy of feed water : 85 kCal/Kg
Quantity of fuel Consumed : 1.6 TPH
GVC of Coal : 4000 Kcal/Kg
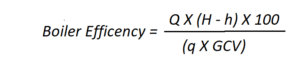
Were
Q = Quantity of steam generated per hour (kg/hr)
Q = Quantity of fuel used per hour (kg/hr)
GCV = Gross calorific value of the fuel (kCal/Kg)
H = Enthalpy of steam (Kcal/kg)
h = Enthalpy of water (Kcal/kg)
![]()
Evaporation Ratio = 8 tones of steam / 1.6 tones of coal = 5
Now, In the indirect method, all the heat losses of a boiler are measured and its efficiency computed by subtracting the losses from the maximum of 100.
For small capacity boilers, direct method can be attempted, but it is preferable to conduct indirect efficiency evaluation, since an indirect method permits assessment of all losses and can be a tool for loss minimization.
We will learn the calculation of boiler efficiency through indirect method in our next chapter. Keep visiting Avlon-php.com for more information. We are one of the best Boiler contractor Philippines dealing in both small and large series of boilers